
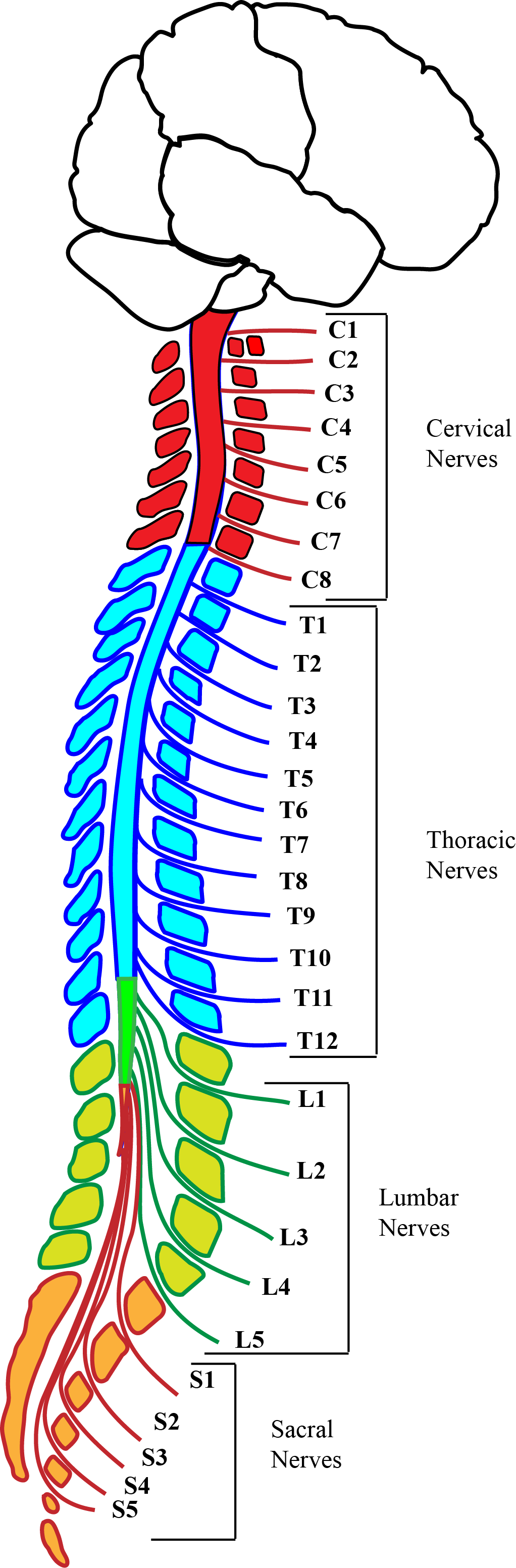
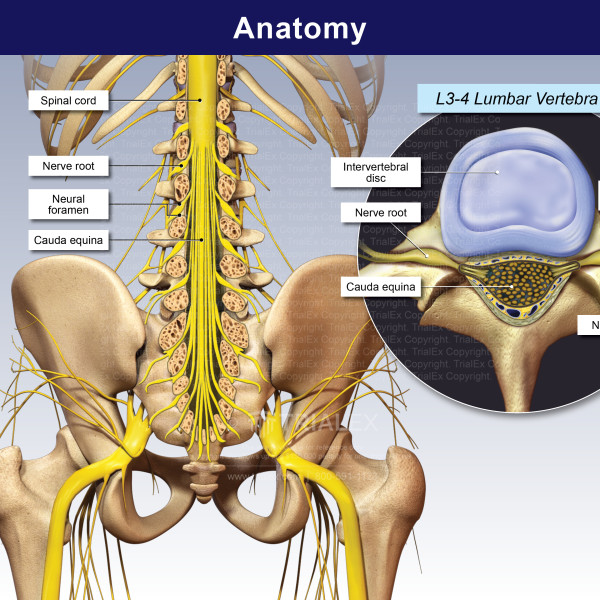
It provides several important functions, including: This bundle is called the cauda equina.The human spine is a complex anatomic structure that is the scaffolding for the entire body. Beyond that, it is a bundle of nerves and roots that are more exposed than the nerves residing above. The spinal cord ends after the first lumbar (low back area) vertebra. Spinal nerve roots exit the spaces (called intervertebral foramina) created between two adjacent, stacked vertebrae. The first branch into spinal nerve roots (already discussed) and then further subdivide into nerves that go to all parts of the body to pick up sensory information and relay that to the brain, as well as deliver movement instructions and impulses from the brain to the muscles. Spinal nerves arise from the spinal cord at each level. The spinal cord runs through the center passageway (spinal canal, already discussed) that is made by the bony rings of the stack of vertebrae. Holes located on the sides of the column (called neuralforamina, discussed above) are made by the interfacing vertebrae nerve roots exit out these holes, and depending on the condition of the bone around them, they may play an important role in the presence or absence of back pain.Įxamples of common back problems involving the spinal nerve root include herniated disc and spinal stenosis. When you count the sacrum and coccyx, the spine is a long flexible column made of 26 interconnected bones. Left unchecked, a pars defect can develop into spondylosis and finally spondylolisthesis, where one bone becomes destabilized to the point of slipping either forward or back of the bone next to it. (Middle-aged people, especially those who are overweight are also at risk for a pars defect). The initial injury is called a pars defect it's brought on by repeated spinal movements such as those done by athletes. Problems with facet joints are a very common cause of back pain and generally are associated with spinal arthritis and/or degenerative spinal changes.Īnother back problem called spondylolisthesis often starts with a small fracture in an obscure area of the facet joint known as the pars. That's a difficult word to pronounce, so many people, including healthcare providers, prefer the term "facet joint."
The interconnected aspect of facet joint construction makes it a key player for keeping the entire spinal column stable during movement.įacet joints are also called the zygapophyseal joints. The processes that make up the facet joint are called the "articular processes." This means 4 of these processes participate to construct the facet joints at any one level, or segment, of the spine. At each level (called a "segment,") there's a right and left facet joint. It is formed by processes (which are basically extensions of bone) that emanate from an interconnected pair of adjacent vertebrae-one above and below. The facet joint is located on the bony ring in the back of the spinal column. It also contributes to the vertebral endplate, which can be another site of degenerative spinal changes. The vertebral body defines part of the edge of the central area in the spinal column through which the spinal cord passes. The intervertebral disc is often the first place in the spine where age-related degenerative changes (which pretty much everyone gets) take place. An annular tear is another injury that may lead to a herniated disc, but not always. They do this by acting as a movable cushion between the vertebral bodies.Ĭommon disc problems include disc degeneration and herniated disc. In between the vertebral bodies are the intervertebral discs, which are responsible for shock absorption during movement. The vertebrae stack on top of one another at the vertebral bodies. The vertebral body is the largest and most supportive part of the vertebra.Īs discussed above, the vertebral body is a large roundish structure that provides weight support through the column.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
